After smoking, radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer in the United States. Radon is a naturally occurring, colorless and odorless radioactive gas, formed by the radioactive decay of Uranium. Radon can enter homes where it is inhaled by the occupants of the house putting them at risk. The EPA estimates that Radon is responsible for about 21,000 lung cancer deaths every year. About 2,900 of these deaths occur among people who have never smoked. Concentrations of Radon above what the EPA has determined to be the “Action Level” 4.0pCi/l have been detected in homes throughout the US can be readily corrected by the installation of Radon Remediation Systems.
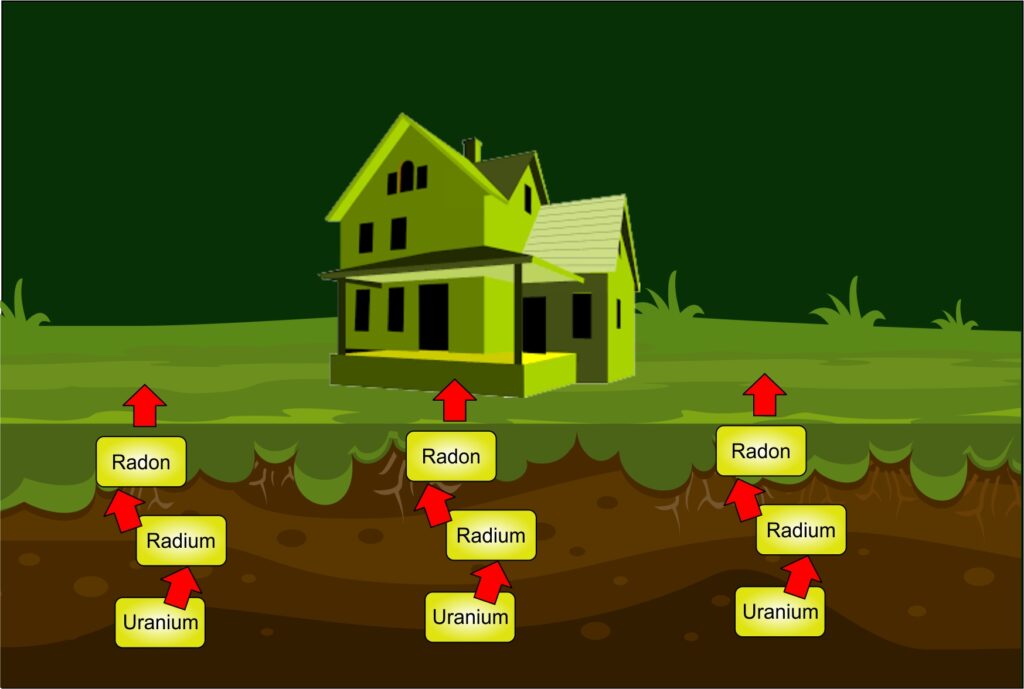
Any home can have a radon problem regardless of whether it is new or old, well sealed of drafty, or if it has a basement or not. The estimate of the EPA is that one in 15 homes throughout the US have radon concentrations above the action level.

Radon levels can be lowered through a variety of repairs from sealing cracks in foundations, floors, and walls to changing the flow of air into the building. Sub-slab depressurization uses pipes and fans to remove Radon gas from beneath the concrete floor and foundation before it can enter the building. Radon is then vented above the roof where it safely disperses. Repairs to decrease Radon levels should be made by an EPA or state-certified contractor.
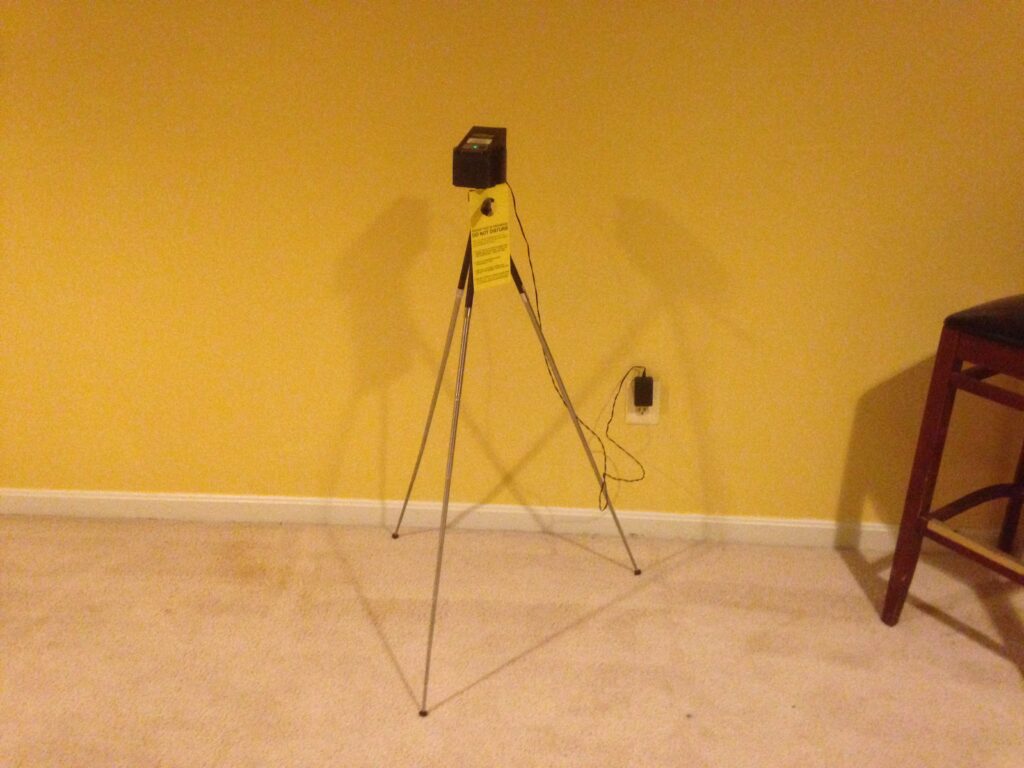

Since radon is colorless and odorless the only way to your home’s radon levels is to test. Exposure to radon causes no immediate symptoms and it typically takes years of exposure before any problems surface. The US EPA, Surgeon General, American Medical Association, the American Lung Association all recommend testing your home for radon because testing is the only way to determine if you at are higher risk because of your home’s radon levels.